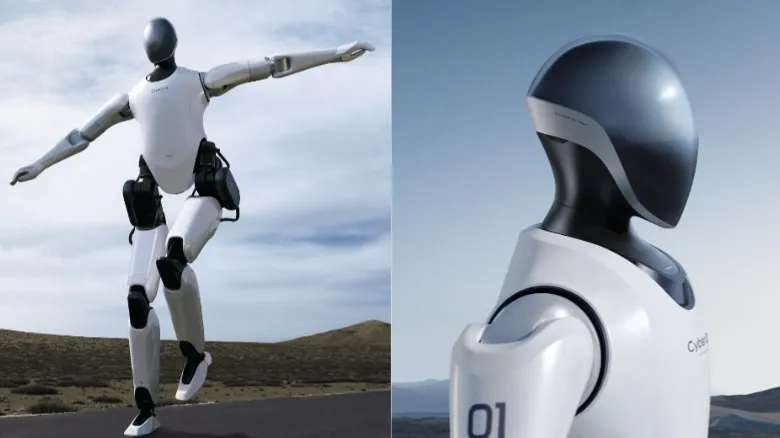
The Xiaomi CyberOne humanoid robot has captured imaginations worldwide with its impressive drumming skills, emotion recognition capabilities, and sleek design that rivals science fiction movies. But if you’re hoping to buy one for your business or research project, prepare for a massive reality check that will fundamentally change how you think about accessing humanoid robotics technology.
Here’s what Xiaomi doesn’t want you to focus on: while CyberOne dominates tech headlines with its advanced capabilities, the robot carries an eye-watering price tag of $89,000-$104,000 with absolutely no commercial release date announced. CEO Lei Jun himself admits mass production remains “still a long way off,” leaving thousands of potential buyers in indefinite limbo while their automation needs go unmet.
But here’s the game-changing secret that smart businesses have discovered: while everyone else waits for CyberOne’s eventual commercial release, forward-thinking companies are already deploying humanoid robotics through accessible rental programs that cost a fraction of CyberOne’s price tag. If you’re tired of waiting for promises and want actual robots working in your facility today, this comprehensive analysis reveals exactly what’s available now and why the alternative might be better than what you’re waiting for.
Xiaomi CyberOne Humanoid Robot: The $89K Reality Check
The Xiaomi CyberOne humanoid robot represents one of the most sophisticated pieces of robotics technology ever developed, but its pricing structure places it firmly in the “corporate fantasy” category for most potential buyers. When you see those viral videos of CyberOne playing drums or recognizing human emotions, you’re looking at a machine that costs more than most people’s annual salaries.
Recent comprehensive research reveals that CyberOne’s current unit costs range from $89,000 to $104,000, positioning it among the most expensive humanoid robots in development today. This pricing reflects the robot’s advanced technical specifications, including 21 degrees of freedom across 13 joints, sophisticated AI processing through dual Intel i7 Xeon quad-core computers, and custom actuators providing up to 300 Nm instantaneous peak torque for hip joints.
The Premium Technology Tax CyberOne’s astronomical pricing stems from its cutting-edge components and limited production runs. The robot features proprietary Mi-Sense depth vision modules that enable 3D space perception with 99% accuracy at ranges up to 8 meters, while advanced AI engines provide environmental semantics recognition across 85 sound types and 45 human emotion classifications. These specifications exceed most competitors but come at premium prices that reflect research and development costs rather than mass production economics.
Manufacturing Reality vs. Marketing Promises While Xiaomi showcases CyberOne’s impressive capabilities, the company maintains complete internal control over development through its dedicated Robotics Lab, with no external sales or distribution channels established. Current production remains limited to research and development units with no mass production timeline announced for commercial availability.
The pricing reality becomes even more challenging when you factor in the total cost of ownership. Like all sophisticated robotics platforms, the $89,000-$104,000 purchase price represents only the beginning of your investment, with integration, training, and ongoing support costs typically adding 50-80% to initial expenditures.
This pricing structure explains why most organizations interested in humanoid robotics are exploring alternative approaches that provide access to advanced capabilities without the crushing financial commitment that CyberOne requires.
Why Xiaomi CyberOne Costs More Than a Tesla Model S
The sticker shock of Xiaomi CyberOne’s $89,000-$104,000 price tag becomes even more dramatic when you compare it to luxury automobiles, revealing why this humanoid robot remains financially out of reach for most potential buyers despite its impressive technical capabilities.
Premium Component Integration CyberOne’s high costs reflect sophisticated engineering integration that surpasses most consumer products. The robot’s custom high-efficiency motors provide 30 Nm rated output torque for upper limbs while achieving 96 Nm/kg power density through precision manufacturing that requires specialized facilities and quality control processes. These custom actuators alone cost more than many complete consumer robots.
Advanced AI Processing Infrastructure The robot’s computational requirements demand enterprise-level hardware including dual Intel i7 Xeon quad-core computers and NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX processing units, with custom DSP-based controllers on each joint. This processing power enables real-time response speeds of 0.5 milliseconds per joint, but requires hardware configurations that cost tens of thousands of dollars before assembly and integration.
Research vs. Production Economics Unlike Tesla vehicles that benefit from mass production economies, CyberOne remains in limited research and development production runs that eliminate cost advantages from scale manufacturing. Xiaomi’s manufacturing approach emphasizes quality control and safety testing before broader deployment, with conservative production volumes that maintain high per-unit costs.
Ecosystem Integration Premiums CyberOne’s integration with Xiaomi’s broader technology ecosystem requires specialized software development and testing that adds significant costs to each unit. The robot’s ability to interface with Xiaomi’s IoT products, smartphones, and HyperOS platform demands extensive compatibility testing and custom programming that inflates development costs.
The Competitive Context This pricing positions CyberOne significantly above Tesla’s Optimus, which targets $20,000-$30,000 at scale, and far beyond accessible options like the Unitree G1 starting at $16,000. The cost differential reflects CyberOne’s research platform focus rather than commercial market positioning.
The luxury car comparison highlights a fundamental disconnect: while a Tesla Model S provides immediate transportation value, CyberOne’s high price buys access to experimental technology with uncertain commercial applications and no clear deployment timeline.
Xiaomi CyberOne ROS: Advanced Tech, Zero Availability
The most frustrating aspect of Xiaomi CyberOne for potential buyers isn’t the high price – it’s the complete lack of availability for commercial purchase. Despite impressive technical demonstrations and widespread media coverage, CyberOne remains locked within Xiaomi’s internal development ecosystem with no clear path to market access.
Internal Deployment Strategy Recent developments in June 2024 show Xiaomi actively promoting phased implementation of CyberOne within its own manufacturing systems, representing a shift from demonstration to practical industrial application. However, this internal deployment strategy specifically excludes external sales, with the company relocating its robotics division to the Xiaomi Automobile Factory in Beijing Yizhuang to focus on controlled testing environments.
ROS Integration Limitations While CyberOne demonstrates advanced Robot Operating System (ROS) integration capabilities, these features remain accessible only to Xiaomi’s internal development teams. The robot’s sophisticated bipedal control algorithms and custom actuator systems that enable precise movement coordination aren’t available for external developers or researchers who might benefit from ROS compatibility.
No Commercial Timeline CEO Lei Jun’s acknowledgment that mass production remains “still a long way off” effectively eliminates CyberOne as a viable option for organizations needing humanoid robotics capabilities today. The company’s conservative approach prioritizes internal testing and development over commercial availability, leaving potential buyers in indefinite waiting periods.
Enterprise Access Restrictions Unlike competitors who offer limited commercial access or pilot programs, Xiaomi maintains strict control over CyberOne access. The robot’s three-phase deployment approach begins with internal testing, progresses to selective enterprise applications by 2025-2027, and eventually anticipates broader market expansion as costs decrease – timelines that offer no immediate solutions for current robotics needs.
Technical Capabilities Without Access CyberOne’s impressive technical specifications become irrelevant when access remains restricted. The robot’s ability to recognize 85 environmental sounds and 45 human emotions represents breakthrough capabilities that could benefit numerous applications, but these features remain locked within Xiaomi’s development environment.
This availability gap creates the perfect opportunity for smart buyers to access similar capabilities through alternative platforms that are actually available for deployment today.
The Xiaomi CyberOne Release Date That May Never Come
Xiaomi’s approach to CyberOne commercialization reveals a timeline so conservative that potential buyers face the very real possibility that widespread availability may never materialize, making waiting for CyberOne a potentially endless exercise in delayed automation plans.
The “Long Way Off” Reality CEO Lei Jun’s frank admission that mass production remains “still a long way off” represents one of the most honest assessments in the robotics industry, where companies typically provide optimistic timelines that rarely materialize. This acknowledgment suggests Xiaomi recognizes significant technical and economic challenges that require years of additional development before commercial viability.
Three-Phase Timeline Uncertainty Xiaomi’s conservative three-phase approach provides no concrete dates for any deployment stage. Phase 1 focuses on internal testing within Xiaomi facilities with undefined duration. Phase 2 involves selective enterprise applications targeting sub-$50,000 pricing by 2025-2027 – a two-year window that could easily extend further. Phase 3 anticipates broader market expansion only as costs decrease significantly, with no timeline or price targets announced.
Manufacturing Complexity Barriers The transition from prototype to commercial production involves challenges that have derailed numerous robotics companies. CyberOne’s sophisticated mechanical systems require precision manufacturing capabilities that scale poorly from research quantities to commercial volumes. The robot’s custom actuators, advanced AI processing requirements, and integration complexity create manufacturing bottlenecks that could extend development timelines indefinitely.
Market Readiness Questions Even if Xiaomi resolves manufacturing challenges, market readiness for $89,000+ humanoid robots remains questionable. The company’s strategy of reducing costs through optimized material usage and streamlined manufacturing processes could take years to achieve meaningful price reductions, particularly without clear demand signals from potential commercial buyers.
Competitive Pressure Reality While Xiaomi develops CyberOne internally, competitors are advancing rapidly toward commercial deployment. Tesla’s Optimus targets commercial availability by 2026, while companies like Unitree are already shipping humanoid robots today. This competitive pressure could force Xiaomi to rush development or abandon commercial plans if the market moves beyond their timeline.
Government Support Dependency CyberOne’s development relies heavily on China’s national humanoid robot mass production goals and $1.4 billion robotics development funds. Policy changes or funding reductions could impact development timelines, making commercial availability dependent on political priorities rather than market demand.
The combination of conservative timelines, technical complexity, and external dependencies suggests that waiting for CyberOne commercial availability represents a high-risk strategy for organizations needing humanoid robotics capabilities.
Xiaomi Roboter Humanoid vs. What’s Actually Available Now
While Xiaomi CyberOne captures headlines with impressive demonstrations, the practical reality for businesses needing humanoid robotics today requires comparing theoretical future availability against actual deployment options that exist in the current market.
Specification Comparison Reality CyberOne’s impressive specifications include 177 cm height, 52 kg weight, and 21 degrees of freedom with advanced emotion recognition across 45 human classifications. However, these capabilities remain locked within Xiaomi’s development environment while comparable robots like the Unitree G1 offer 23-43 degrees of freedom, sophisticated locomotion, and actual commercial availability starting at $27,300.
Availability Timeline Contrast The fundamental difference between CyberOne and available alternatives isn’t technical capability – it’s timeline. While Xiaomi’s conservative approach keeps CyberOne in indefinite development phases, the Unitree G1 ships immediately with comprehensive support, training, and integration assistance. This availability gap means organizations choosing currently available options gain months or years of operational experience while CyberOne buyers remain in waiting periods.
Practical Application Focus CyberOne’s design emphasizes ecosystem integration with Xiaomi’s IoT products and consumer-focused features like emotion recognition and interactive displays. Available alternatives like the G1 focus on practical business applications including locomotion, manipulation, and integration with existing workflows – capabilities that deliver immediate value rather than theoretical future benefits.
Cost Structure Analysis Even when CyberOne eventually reaches commercial availability, its projected pricing of $89,000-$104,000 positions it as a premium research platform rather than a practical business tool. Current alternatives provide humanoid robotics capabilities at fraction of CyberOne’s costs, with rental options starting at $1,800 monthly that include comprehensive support and maintenance.
Technical Maturity Levels CyberOne represents cutting-edge research with impressive demonstrations but limited practical deployment experience. Available alternatives benefit from real-world testing, user feedback, and iterative improvements based on actual commercial deployments rather than controlled laboratory environments.
Integration and Support Ecosystems Xiaomi’s focus on internal development means limited external support ecosystems for CyberOne integration and maintenance. Available robots benefit from established dealer networks, technical support infrastructures, and growing communities of users and developers who provide practical implementation guidance.
The choice between waiting for CyberOne’s eventual availability and deploying currently available alternatives ultimately depends on whether organizations prioritize cutting-edge demonstrations or practical robotics capabilities that can be implemented today.
While You Wait for CyberOne: Smart Businesses Do This Instead
The indefinite timeline for Xiaomi CyberOne commercial availability has created a massive opportunity gap that forward-thinking businesses are filling through alternative approaches to humanoid robotics access. Rather than waiting for promises, these organizations are gaining competitive advantages through strategies that provide immediate access to advanced robotics capabilities.
The Rental Revolution Smart businesses have discovered that rental access to humanoid robots provides superior value compared to waiting for expensive purchases that may never materialize. Monthly rental costs of $1,800-$3,200 for fully capable humanoid robots deliver immediate access to automation capabilities while preserving capital for core business investments and avoiding the risks associated with emerging technology purchases.
Test-to-Own Strategies Rather than betting tens of thousands of dollars on theoretical robot capabilities, successful organizations use test-to-own programs that provide months of real-world experience before making purchase commitments. This approach eliminates the biggest risk in robotics adoption: discovering expensive equipment doesn’t deliver expected value in specific operational environments.
Competitive Advantage Through Early Adoption While competitors remain stuck in analysis paralysis waiting for “perfect” solutions like CyberOne, early adopters are gaining practical experience with humanoid robotics that translates into operational improvements, team training, and competitive positioning. This experience gap compounds over time, creating sustainable advantages for organizations that act rather than wait.
Technology Evolution Alignment The robotics industry evolves rapidly, with significant improvements emerging every 12-18 months. Organizations using rental access models automatically benefit from technology upgrades and capability improvements, while buyers locked into specific purchases watch their expensive investments become obsolete as better options emerge.
Risk Management Through Flexibility Current rental programs eliminate downside risk by allowing termination if robots don’t deliver expected value, while providing upgrade pathways when better technology becomes available. This flexibility contrasts sharply with purchase approaches that lock organizations into expensive decisions based on incomplete information and uncertain outcomes.
Operational Learning While Waiting Even organizations eventually planning to purchase premium robots like CyberOne benefit from current operational experience with available alternatives. This learning process helps identify optimal applications, develop team expertise, and refine integration approaches that improve eventual premium robot deployments.
Content and Marketing Advantages Businesses using humanoid robots today gain significant marketing and content advantages that waiting for future technology can’t provide. These organizations showcase cutting-edge capabilities, attract media attention, and position themselves as innovation leaders while competitors remain stuck in research modes.
The smart money recognizes that access to current technology beats waiting for theoretical future solutions, especially when rental models provide low-risk pathways to immediate capability gains.
Xiaomi CyberOne Manufacturing Deployment: Why It Doesn’t Help You
Xiaomi’s announcement of CyberOne deployment within its own manufacturing facilities represents significant technical progress, but this internal implementation strategy actually highlights why the robot remains irrelevant for external buyers seeking humanoid robotics solutions for their own operations.
Internal-Only Strategy Limitations Xiaomi’s June 2024 promotion of phased CyberOne implementation specifically targets the company’s own manufacturing systems, with no indication that this deployment experience will translate into external commercial availability. The robot’s relocation to the Xiaomi Automobile Factory in Beijing Yizhuang places it within a controlled ecosystem that explicitly excludes outside access or learning opportunities.
Controlled Environment Dependency CyberOne’s manufacturing deployment success depends heavily on Xiaomi’s specific operational environment, custom integration systems, and dedicated technical support teams. These controlled conditions don’t translate to typical business environments where organizations lack Xiaomi’s extensive robotics expertise, custom infrastructure, and unlimited technical support resources.
No Knowledge Transfer Mechanisms Unlike traditional technology companies that leverage internal deployments to refine products for external sales, Xiaomi maintains strict separation between internal CyberOne usage and potential commercial applications. The company’s vertically integrated approach means insights from manufacturing deployment remain proprietary rather than informing commercial product development.
Technical Specifications vs. Real-World Performance Manufacturing deployment allows Xiaomi to showcase CyberOne’s technical capabilities in optimal conditions, but provides no indication of how the robot performs in diverse environments with varying infrastructure, support levels, and application requirements. This deployment experience may actually increase Xiaomi’s confidence in maintaining high prices and limited availability.
Timeline Implications Rather than accelerating commercial availability, internal manufacturing deployment could extend development timelines as Xiaomi focuses on optimizing CyberOne for its specific operational needs rather than developing commercially viable versions for diverse markets. The company’s investment in internal deployment infrastructure reduces incentives for external commercialization.
Learning Curve Exclusion External organizations can’t benefit from Xiaomi’s manufacturing deployment experience, meaning potential buyers must start their robotics learning curves from zero when alternatives eventually become available. This exclusion widens the gap between organizations with current robotics experience and those waiting for premium solutions.
Alternative Deployment Experience While Xiaomi develops internal expertise with CyberOne, organizations using currently available robots gain practical deployment experience, team training, and operational optimization knowledge that provides competitive advantages regardless of future technology developments.
The manufacturing deployment announcement ultimately emphasizes CyberOne’s exclusivity rather than its accessibility, reinforcing why smart businesses choose available alternatives over waiting for internal development programs.
$104,000 CyberOne vs. $1,800/Month G1: The Math is Shocking
The financial comparison between Xiaomi CyberOne’s premium pricing and accessible rental alternatives reveals a cost differential so dramatic that it fundamentally changes how smart buyers approach humanoid robotics investment decisions.
Purchase Price vs. Access Cost Analysis CyberOne’s $104,000 maximum pricing represents the equivalent of 57 months of G1 rental at $1,800 monthly – nearly five years of humanoid robotics access without any upfront capital commitment. This comparison becomes even more favorable when factoring in the comprehensive support, maintenance, and upgrade benefits included in rental programs that CyberOne buyers must handle separately.
Total Cost of Ownership Reality The $104,000 CyberOne purchase price represents only the beginning of ownership costs. Professional robotics implementations typically require additional investments of 60-80% beyond purchase price for integration, training, facility modifications, and ongoing support. CyberOne’s sophisticated systems likely require premium support contracts, specialized training, and custom integration work that could easily add $50,000-$80,000 to total first-year costs.
Technology Evolution Economic Impact CyberOne buyers face immediate depreciation as robotics technology advances rapidly. The $104,000 investment becomes a sunk cost that declines in value while rental customers automatically access improved technology, software updates, and capability enhancements without additional investment. Over five years, this technology evolution benefit could represent $30,000-$50,000 in value for rental customers.
Risk Management Value Quantification Purchase approaches carry significant downside risk if robots don’t deliver expected value in specific environments. A $104,000 CyberOne investment that fails to meet operational requirements represents a catastrophic loss, while rental programs eliminate this risk through termination options that cap losses at monthly fees rather than total purchase prices.
Opportunity Cost Calculations The $104,000 capital investment in CyberOne could generate approximately $5,200 annually in conservative investment returns at 5% rates. Over five years, this opportunity cost adds $26,000 to the true cost of robot ownership, while rental preserves capital for core business investments that might deliver superior returns.
Operational Flexibility Premium Rental models provide scaling flexibility that purchase approaches can’t match. Organizations can adjust robot usage based on seasonal demands, project requirements, or changing business priorities without being locked into expensive capital assets that become anchors during business pivots.
Cash Flow and Balance Sheet Advantages Monthly rental expenses of $1,800 fall within operational budgets that don’t require board-level capital expenditure approvals, while $104,000 purchases typically require extensive justification and approval processes that delay implementation timelines.
The mathematical reality demonstrates that rental access provides superior financial returns, lower risk exposure, and greater operational flexibility compared to premium robot purchases like CyberOne.
Xiaomi CyberOne Drumming Skills vs. Real Business Applications
Xiaomi’s viral marketing of CyberOne’s drumming capabilities exemplifies a fundamental disconnect between impressive technical demonstrations and practical business applications that actually deliver measurable value to organizations considering humanoid robotics investments.
Marketing Spectacle vs. Practical Value CyberOne’s ability to parse MIDI files into synchronized drum beats requiring precise timing represents sophisticated engineering achievement, but this capability provides minimal value for most business applications. The drumming demonstration showcases whole-body coordination and temporal precision, but organizations need robots that handle material movement, quality inspection, and assembly tasks rather than musical performances.
Technical Capability Translation Challenges While the drumming research highlights progress in coordinated motion control essential for manufacturing applications, the gap between playing drums and performing practical business tasks remains substantial. Drumming requires repetitive precision in controlled environments, while real business applications demand adaptability, problem-solving, and integration with existing workflows.
Resource Allocation Questions Xiaomi’s investment in developing drumming capabilities raises questions about development priorities when fundamental business applications remain unaddressed. Organizations need robots that can navigate diverse environments, manipulate varied objects, and integrate with existing systems – capabilities that require different engineering focus than musical performance optimization.
Alternative Approach Comparison Available humanoid robots like the Unitree G1 focus development resources on practical business capabilities including locomotion, manipulation, and environmental navigation. These robots may lack CyberOne’s drumming skills but provide immediate value for applications like facility inspection, material handling, and automated assistance that directly impact business operations.
Demonstration vs. Deployment Reality CyberOne’s drumming demonstrations occur in controlled laboratory environments with optimal conditions, specialized equipment, and unlimited technical support. Real business deployments require robots that perform reliably in varied conditions with limited technical support and integration with existing operational constraints.
Marketing Investment vs. Commercial Readiness The resources devoted to creating viral drumming content could alternatively focus on developing commercial viability, reducing costs, or improving practical applications. This marketing investment strategy suggests Xiaomi prioritizes technology demonstration over commercial accessibility.
Customer Need Alignment Potential robot buyers need solutions for specific business challenges rather than impressive technical demonstrations. Organizations considering humanoid robotics typically focus on productivity improvements, labor shortage solutions, and operational efficiency gains rather than entertainment capabilities or technical showcases.
The drumming capability disconnect illustrates why smart buyers focus on robots that address actual business needs rather than waiting for premium platforms optimized for technical demonstrations that may never translate into practical commercial value.
Why CyberOne’s “Phase 1 Testing” Means Years of Waiting
Xiaomi’s conservative three-phase deployment strategy for CyberOne effectively guarantees that potential commercial buyers face years of indefinite waiting before gaining access to the technology, making alternative approaches essential for organizations needing humanoid robotics capabilities today.
Phase 1 Internal Testing Duration Uncertainty Xiaomi’s Phase 1 strategy focuses on internal testing and development within company facilities with no announced timeline for completion. This internal focus could extend indefinitely as the company refines capabilities, addresses technical challenges, and optimizes integration with existing manufacturing systems. Industrial robotics testing typically requires 18-36 months minimum, suggesting Phase 1 alone could consume years of development time.
Phase 2 Limited Enterprise Access The projected Phase 2 timeline of 2025-2027 for selective enterprise applications provides a two-year window that could easily extend further based on Phase 1 results. Even within this timeline, “selective” enterprise access suggests extremely limited availability with unknown qualification criteria, pricing structures, or geographic restrictions that could exclude most potential buyers.
Phase 3 Mass Market Fantasy Phase 3 anticipates broader market expansion only as costs decrease significantly, with no timeline, price targets, or availability commitments announced. This phase depends entirely on successful completion of Phases 1 and 2, plus resolution of cost reduction challenges that have proven difficult for most robotics companies to achieve at scale.
Technical Refinement Requirements CyberOne’s sophisticated mechanical systems and advanced AI integration require extensive real-world testing to identify and resolve reliability issues, safety concerns, and operational limitations. The complexity of humanoid robotics means testing phases typically reveal unexpected challenges that extend development timelines beyond initial projections.
Manufacturing Scale Challenges Transitioning from limited research production to commercial manufacturing involves scaling challenges that have derailed numerous robotics companies. CyberOne’s custom actuators, precision manufacturing requirements, and quality control standards create bottlenecks that could require years to resolve even after technical development completion.
Competitive Market Evolution While Xiaomi progresses through multi-year testing phases, competitors continue advancing toward commercial availability. Tesla targets Optimus commercialization by 2026, while companies like Unitree ship robots today. This competitive pressure could force Xiaomi to either rush development or abandon commercial plans if markets move beyond their timeline.
Regulatory and Compliance Delays Commercial deployment requires regulatory approvals, safety certifications, and compliance documentation that add additional time requirements beyond technical development. These processes typically require 12-24 months for complex robotics systems, further extending commercial availability timelines.
The multi-phase approach essentially guarantees that CyberOne commercial availability remains years away, making current alternatives essential for organizations that can’t afford indefinite waiting periods for theoretical future access.
The CyberOne Ecosystem Dream vs. Rental Reality
Xiaomi’s vision of CyberOne integration with their broader technology ecosystem represents an ambitious long-term strategy, but this ecosystem dependency actually highlights why rental access to available robots provides more immediate and practical value for most organizations.
Ecosystem Lock-In Limitations CyberOne’s integration with Xiaomi’s “Human x Car x Home” ecosystem strategy requires organizations to adopt Xiaomi’s entire technology stack including smartphones, IoT devices, vehicles, and appliances through HyperOS platform integration. This ecosystem dependency limits CyberOne’s utility for organizations using alternative technology platforms or preferring vendor-neutral robotics solutions.
Commercial Ecosystem Availability The ecosystem integration promise depends on Xiaomi’s broader product availability and market penetration in specific regions. Organizations in markets where Xiaomi’s ecosystem products have limited availability or support can’t realize the theoretical integration benefits that justify CyberOne’s premium pricing and complexity.
Integration Timeline Dependencies Even when CyberOne eventually reaches commercial availability, ecosystem integration benefits require simultaneous access to Xiaomi’s complete product portfolio plus development time for custom integration work. These dependencies could add months or years to implementation timelines while organizations wait for ecosystem components to align.
Practical Application Priority Most organizations need humanoid robots for specific practical applications rather than ecosystem integration showcases. Available alternatives like the Unitree G1 focus on immediate business value including locomotion, manipulation, and task automation that deliver measurable results without requiring complex ecosystem dependencies.
Vendor Independence Advantages Rental access to available robots provides vendor independence that ecosystem approaches can’t match. Organizations can integrate robots with existing technology infrastructure, maintain operational flexibility, and avoid lock-in effects that limit future technology choices or strategic options.
Immediate Value vs. Future Promises The ecosystem integration vision requires believing in Xiaomi’s long-term strategy execution plus waiting for commercial availability plus investing in ecosystem components that may not deliver expected integration benefits. Rental approaches provide immediate access to robot capabilities with proven value rather than theoretical future benefits.
Technology Evolution Flexibility Ecosystem approaches lock organizations into specific technology platforms that may become obsolete or lose competitive advantages over time. Rental models provide flexibility to adapt to technology evolution, change vendors based on performance, and maintain optimal configurations as business needs evolve.
Cost and Complexity Reality Ecosystem integration typically requires premium pricing, complex implementation projects, and ongoing maintenance of multiple technology components. Rental alternatives provide straightforward access to robotics capabilities without ecosystem complexity, integration costs, or vendor dependency risks.
The ecosystem dream ultimately represents vendor lock-in strategy rather than customer value optimization, making rental access to available robots a smarter choice for organizations prioritizing practical results over theoretical integration benefits.
Smart Companies Skip CyberOne Waiting Lists for This Alternative
While the technology industry obsesses over Xiaomi CyberOne’s impressive specifications and ecosystem integration promises, the most successful robotics implementations in 2025 are coming from organizations that chose immediate access over indefinite waiting periods for premium solutions that may never materialize.
The Competitive Advantage Gap Organizations waiting for CyberOne commercial availability are essentially volunteering to fall behind competitors who are gaining practical robotics experience today. Every month spent waiting for theoretical future access represents lost opportunities for team training, workflow optimization, and operational improvements that provide sustainable competitive advantages.
Real-World Implementation Experience Smart companies recognize that robotics success depends more on implementation expertise than robot specifications. Organizations using available alternatives like the Unitree G1 are developing practical knowledge about robot integration, team training, and operational optimization that will benefit any future robotics investments, including eventual premium purchases.
Financial Risk Management The $89,000-$104,000 CyberOne investment represents catastrophic risk if the robot doesn’t deliver expected value in specific environments. Rental alternatives starting at $1,800 monthly eliminate downside risk while providing access to sophisticated humanoid capabilities that often exceed what organizations actually need for their applications.
Technology Evolution Alignment Robotics technology advances rapidly, with significant improvements emerging every 12-18 months. Organizations locked into expensive purchases face obsolescence risk, while rental customers automatically benefit from technology upgrades, software improvements, and capability enhancements without additional investment.
Operational Learning Curves Even organizations eventually planning to purchase premium robots benefit enormously from current operational experience with available alternatives. This learning process helps identify optimal applications, develop team expertise, and refine integration approaches that improve eventual premium robot deployments when they become available.
Market Timing Advantages Early robotics adopters gain market positioning advantages including media attention, customer interest, and innovation leadership that late followers struggle to achieve. Organizations waiting for “perfect” solutions miss these first-mover benefits that often justify robotics investments beyond simple productivity calculations.
Scalability and Flexibility Benefits Rental programs provide scaling flexibility that purchase approaches can’t match. Organizations can adjust robot usage based on seasonal demands, project requirements, or changing business priorities without being locked into expensive capital assets that become constraints during business evolution.
Proven ROI Development Using available robots immediately enables organizations to develop proven ROI models based on real operational data rather than theoretical projections. This experience provides confidence and justification for future robotics investments while demonstrating practical value to stakeholders and budget decision-makers.
The smart money recognizes that immediate access to good robotics technology beats indefinite waiting for perfect solutions, especially when rental models provide low-risk pathways to competitive advantages that waiting strategies simply cannot deliver.
Stop Waiting for CyberOne: Get Humanoid Robots Today
The reality of humanoid robotics in 2025 is clear: while Xiaomi CyberOne captures headlines with impressive demonstrations and promises of future availability, smart businesses are already deploying humanoid robots through accessible rental programs that provide immediate value without the financial risk or indefinite waiting periods that CyberOne requires.
The Waiting Game Ends Here Every day spent waiting for CyberOne’s commercial release is a day your competitors gain operational experience with humanoid robotics that could provide lasting competitive advantages. The projected timeline of 2025-2027 for even limited enterprise access means organizations choosing to wait face years of competitive disadvantage while early adopters optimize workflows, train teams, and develop robotics expertise.
Immediate Access vs. Theoretical Promises While CyberOne remains locked in Xiaomi’s internal development programs, proven alternatives like the Unitree G1 ship immediately with comprehensive support packages. Monthly rental programs starting at $1,800 provide access to sophisticated humanoid capabilities including advanced locomotion, manipulation skills, and AI integration that deliver practical business value today rather than theoretical benefits years in the future.
Risk-Free Testing vs. Expensive Gambles CyberOne’s eventual $89,000-$104,000 price tag represents a massive financial gamble based on marketing demonstrations rather than real-world performance in your specific environment. Rental programs eliminate this risk by providing comprehensive testing periods that let you evaluate robotics capabilities, measure productivity impacts, and develop implementation expertise before making any long-term commitments.
Technology Leadership Through Action The most successful robotics implementations come from organizations that act rather than analyze. Companies using rental access to humanoid robots today are building competitive advantages through practical experience, team development, and operational optimization that waiting strategies simply cannot provide. This experience gap compounds over time, creating sustainable advantages for early adopters.
Smart Financial Strategy The mathematics are clear: $1,800 monthly rental costs provide five years of humanoid robotics access for less than CyberOne’s minimum purchase price, while including comprehensive support, maintenance, and upgrade benefits that robot owners must handle separately. This approach preserves capital for core business investments while providing immediate access to cutting-edge robotics capabilities.
The Future is Available Now While others debate whether to wait for CyberOne’s eventual commercial release, forward-thinking organizations are already experiencing the future of work through humanoid robotics deployment. These companies are developing competitive advantages, building robotics expertise, and positioning themselves as innovation leaders while competitors remain stuck in research and analysis phases.
Your Competitive Decision Point The choice is simple: continue waiting for theoretical access to premium robots that may never reach commercial availability, or begin gaining immediate competitive advantages through proven robotics solutions that are available today. Smart businesses recognize that access to good technology today beats waiting for perfect technology tomorrow.
Ready to stop waiting and start experiencing the future of humanoid robotics? Contact Futurobots today to explore rental programs that provide immediate access to advanced robotics capabilities without the financial risk or indefinite waiting periods that traditional purchasing requires.
References and Sources
Key Recent Sources (2024-2025)
- Manufacturing Integration: Xiaomi plans to integrate its humanoid robot CyberOne in its manufacturing process – Gizmochina
- Factory Floor Transformation: How Xiaomi’s CyberOne might be transforming factory floors – The Blife Movement
- China Manufacturing Plans: China’s AI-powered humanoid robots aim to transform manufacturing – Reuters
Technical Specifications
- Design & Capabilities: Xiaomi humanoid robot CyberOne with artificial intelligence – Designboom
- Technical Details: Xiaomi CyberOne Specifications – Qviro
- Robot Guide: CyberOne Robot Guide – Robots Guide
Original Launch Coverage
- TechCrunch Launch: Meet Xiaomi’s new humanoid robot, CyberOne – TechCrunch
- Tesla Comparison: Xiaomi CyberOne humanoid robot challenges Tesla Optimus – Gizchina
- IEEE Drummer Demo: Xiaomi Robot Drummer – IEEE Spectrum
Market Analysis
- Goldman Sachs Market Report: The global market for robots could reach $38 billion by 2035 – Goldman Sachs
- Pricing Analysis: Humanoid robots are getting cheaper. Can affordability drive adoption? – KrASIA
- China Robotics Strategy: China plans to mass produce humanoids by 2025 – The Robot Report
Use Cases & Applications
- Industrial Applications: Xiaomi CyberOne Use Cases – Qviro
- Humanoid Market Trends: 2024: Year of the Humanoid Robot – Mike Kalil
Quick Reference
- Price Range: $89,000 – $104,000
- Height: 177cm (5.8 feet)
- Weight: 52kg
- Speed: 3.6 km/h walking
- Payload: 1.5kg per hand
- Key Feature: Recognizes 85 sounds + 45 human emotions